RadalyX Technology
The unprecedented X-ray imaging quality enables a variety of scanning modes.
"If our machine does not see what you need, no other does."
Josef Uher, CTO
New generation X-ray image
Compared to common X-ray imaging technologies, such as films or flat panels, we use ADVACAM’s new-generation X-ray detectors, which are also used by US NASA in space at the international ISS station for their unique properties.
These photon-counting imaging detectors are characterized by high resolution, almost unlimited range of grey levels, high sensitivity and spatial resolution imaging and last but not least wider application range.
The advantage of using these advanced detectors is the fact that, thanks to their sensitivity, we are able to use up to half the energy of X-rays compared to existing technologies. This implies higher image resolution, but also lower demands on shielding against leakage of X-rays.
This simplifies, reduces the costs and lightens the construction of shielding chambers.
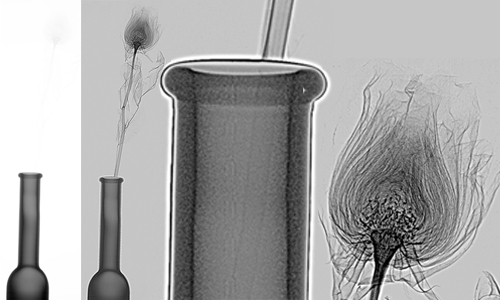
X-ray image of a dry rose demonstrates the unprecedented quality of X-ray imaging. Unlike a standard X-ray device, which is unable to display a dry rose in a vase, an X-ray image of a robotic system using ADVACAM detectors in high resolution and contrast shows both all the delicate parts of the head and even the stem inside the bottle, at the same time!
SOMETHING THAT HAS NOT BEEN POSSIBLE SO FAR!
Combination of imaging methods
ONE MACHINE RULES THEM ALL!
Robots allow to measure 3D images using computed tomography and robosynthesis. Robosytesis is a combination of different computed tomography methods that are applied based on the needs of the resulting image in relation to the size, shape and other parameters of the scanned sample. Commonly used methods in X-ray inspection usually have limited applicability in terms of size or shape of the object. ROBOTS EXCEED THIS LIMIT. The robotic system can also be equipped with a seventh axis (rails) and thus extend the reach of the robotic arm almost without limit.
Mobile Robotic CT
The World´s only CT that "goes" to the sample. The combination of cutting-edge imaging technologies with a pair of robots creates a flexible robotic CT.
3D image of honeycomb structure
The CT scans with RadalyX are possible around nearly any arbitrary axis in 3D. Spectral scan increase recognition possibility of different materials inside for better evaluation (ex. glue distribution).
2D / 3D X-ray imaging in one system
Different types of samples may require different strategies of X-ray scans to capture the required information. The movement flexibility of the two robots extends RadalyX range of 2D and 3D scan approaches.
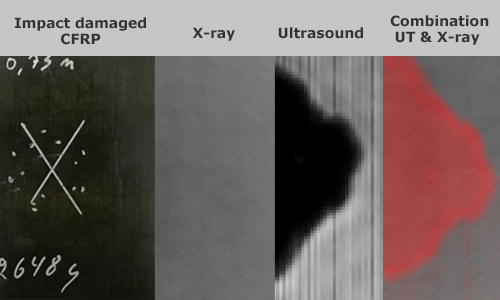
For example, air-coupled ultrasound or Laser Excited Acoustics (LEA) is particularly effective for detecting delaminations in composite materials virtually invisible by X-rays.
A good example is a damaged composite wing of an aircraft after hitting a foreign object. The X-ray image reveals the structure of the composite and its possible damage by fine cracks at the point of impact. However, delamination in the surrounding area cannot be detected by X-ray. Ultrasound is suitable for detecting delamination but does not allow high-resolution imaging of fine cracks.
THE SOLUTION IS A COMBINATION OF BOTH METHODS.

Air-coupled ultrasound (UT)
Radalytica is the first company to prove that X-ray and ultrasound are complementary methods for NDT. In many cases, using more than one method at a time is appropriate to get a better overview of the sample.
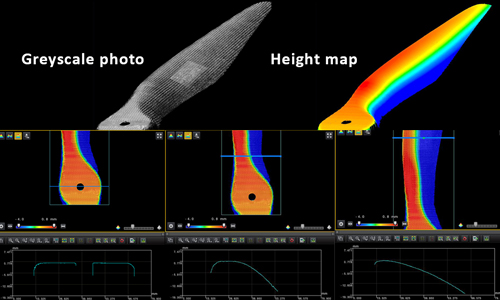
The Robotic Imaging System is equipped with laser distance measurement as standard. It is used by the system to map the shape of the sample before measuring. This information is used to navigate the robots around the sample to avoid collisions. It can also be used to automatically control the trajectory of movement of the robots so that, for example, they maintain a constant distance from the surface and the angle to it. This can be seen i.e. on a curved honeycomb sample, where all honeycomb cells are displayed perpendicularly. In the case of contact methods, robotic arms are also able to maintain a constant pressure on the surface of the sample.
Curved X-ray Scans of Composite Material
Robot automatically scans the sample maintaining the distance and normal to the surface.
Extend and Curve Digital Detector
Bend the detector by robots as you bend digital film by hand.
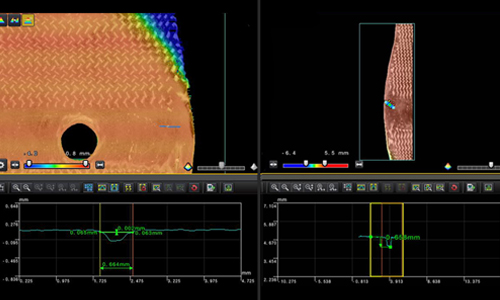
A Parallax free X-ray image
Zoomed parts of the parallel scan image in a pseudo-color map show excessive adhesive and air gaps (left) and a deformed core (right).
The flexibility of robot allows also focusing X-ray images to different depth. We introduce different tomosynthesis scan trajectories to resolve depth information when the accessibility is limited.
The resulting images have correct absolute dimensions at all object depth slices. Due to the limited range of angles, the depth resolution is not as good as in the case of full CT. Therefore, we rather describe the method as a way to ‘focus the X-ray image to a selected depth’.
The full depth data is measured in one scan, and the focused depth is selected easily in the visualization.
THIS CAN BE DONE ON AIRCRAFT!
Lego sample demostration of tomosynthesis
Standard X-ray image is hard to understand. All structures are mixed, figures have different sizes.
Our X-ray imaging system can focus to a selected depth and show different layers of the sample (in this case of the front figure, wall and back figures). Moreover dimensions are correct thus metrology is possible.
Detection of potting compound and its geometry.
The most common means of mechanical attachment in sandwich panels are by potted inserts. Scan reveals the location of the insert and potting compound both in-plane and in-depth.
Electronics inspection
We don't even have to take it out of your bag to see if everything is okay with this laptop.
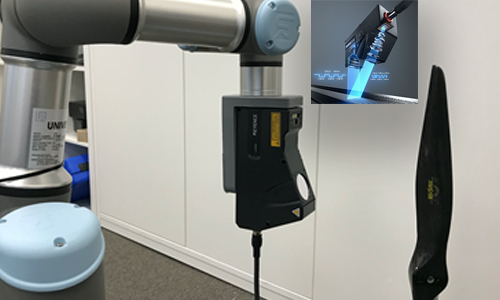
The laser profiler is an imaging tool that provides precise information on scanned object outer shape with precision down to about 30 µm in depth. This tool can be used directly to analyse precision of manufactured parts including their surface structure. The profiler measurements as well as measurements with the other imaging tools are all recorded in the same coordinate space. Therefore, the laser profiler data can also serve as source of outer boundary conditions to improve results of the computed-tomography reconstructions. The profiler uses the quick-mount onto the robot for a quick change of the imaging modalities.
Real-time imaging with a 3D mouse allows full control over the position and viewing angle of the X-ray image. Simply, once you shift and tilt the 3D Mouse Move, the robot tool will follow the same tilt and shift. The X-ray image of the given area of the sample is displayed in real time on the screen. Simple manual control using live view creates the perfect tool for locating defects in the inspected structure in 3D. Therefore, inspection with robots is faster, less demanding on data processing compared to CT and can be applied to the selected areas of larger object.

Intuitive real-time motion response
3D Mouse Move can be used to teach the robots during programming or controlling them in real time to perform tasks.
Real-time imaging
THE GREAT BENEFIT is also the possibility of remote robot control independently of user's location.